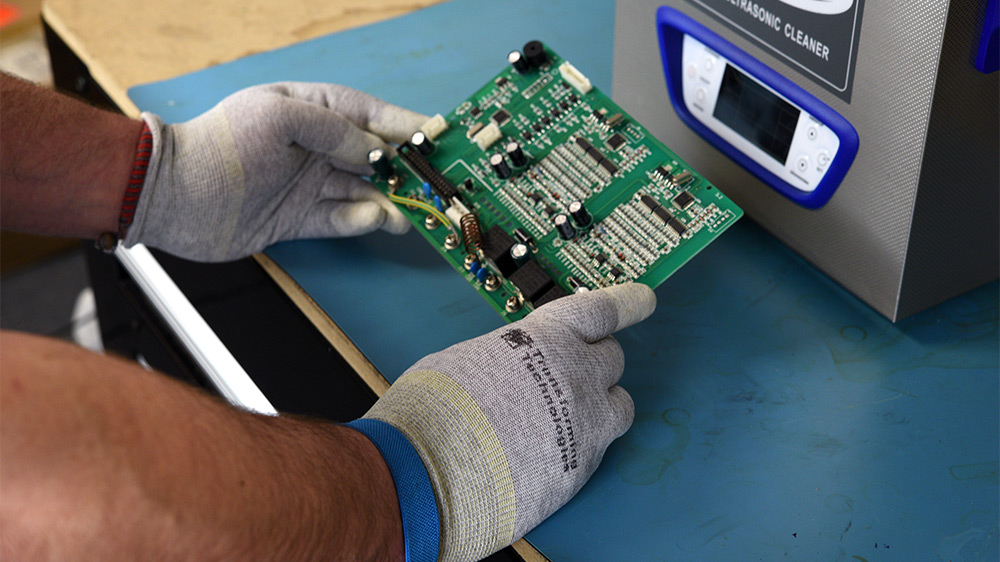
If you were to crack open any electronic device around the house, chances are you'll find what's called a printed circuit board or PCB in there with lots of tiny parts attached to it. These are known as electronic components and they are the building blocks of any electronic circuit. They are bonded to the PCB using soldering techniques.
Let's quickly go over the different types of electronic construction that you may come across.
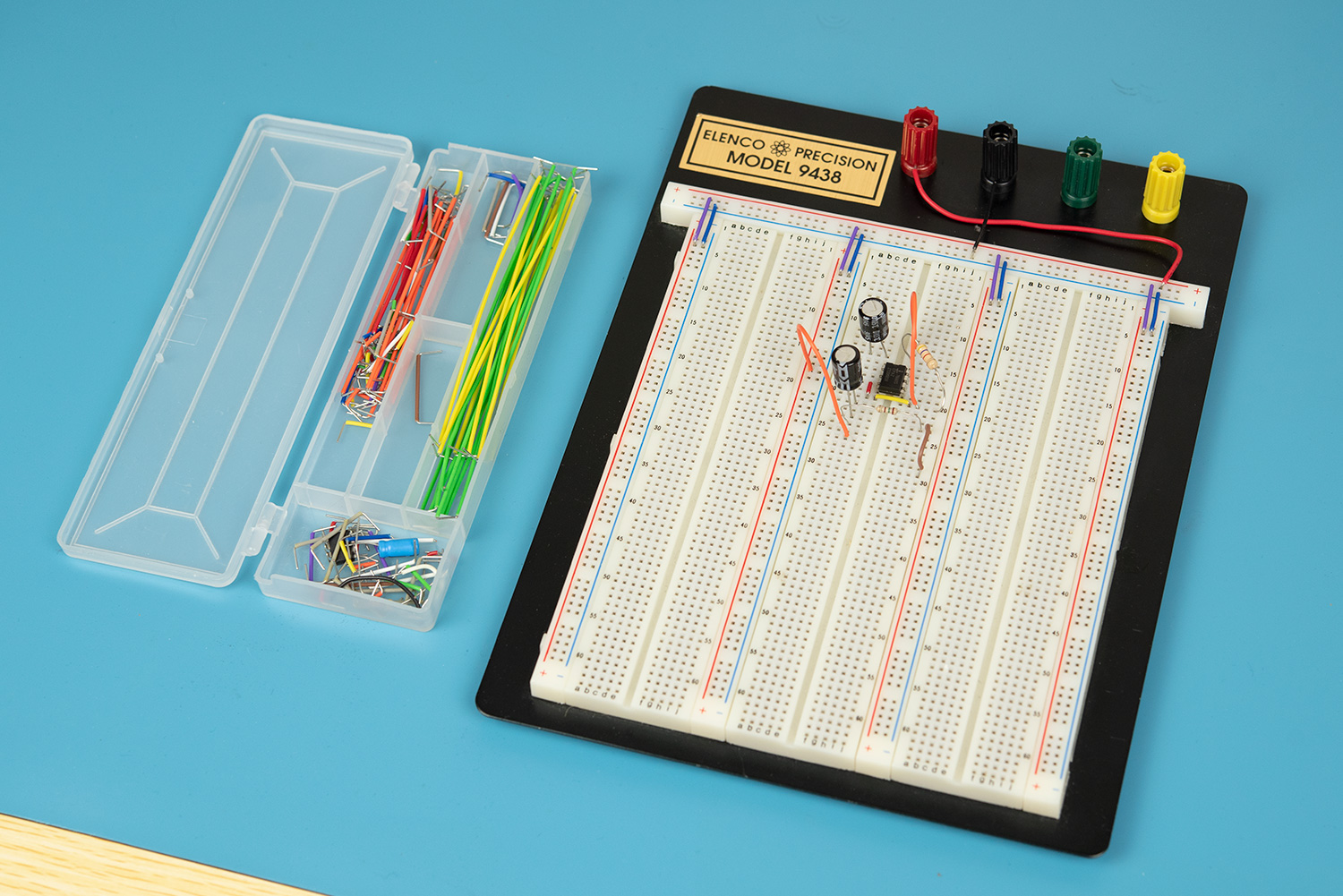
When first conceptualizing a circuit you may want to produce a prototype for testing. This can be done quickest on a breadboard which is a solderless prototyping device with little holes for component leads that are electrically connected by internal busses.
Alternatively you could use computer simulation software like Multi-Sim or TinkerCAD to design and layout your circuit. This is great if you don't have the parts on hand or just want to see the outcome before building. TinkerCAD is free and has components for Arduino builds.
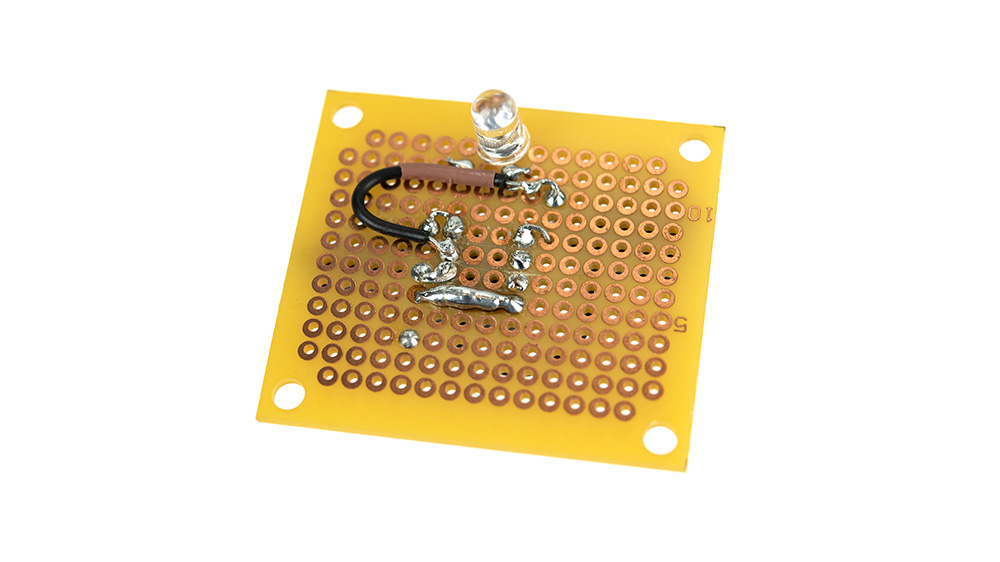
There comes a time where you may want to test your circuits under real-life conditions by creating a soldered prototype. Protoboard or perfboard is perfect for this because it has lots of holes with pads to solder to. The holes are very closely populated allowing you to create solder traces (paths) like a PCB by bridging them with solder for flexible layout options.
Once upon a time before circuit boards, consumer electronics were simpler devices. component leads were simply soldered to each other. Since components are directly connected there is less resistance in the circuit, resulting in the cleanest and strongest signal path possible. For this reason some Hi-Fi audio equipment and amplifiers are still built using point-to-point wiring to this day.
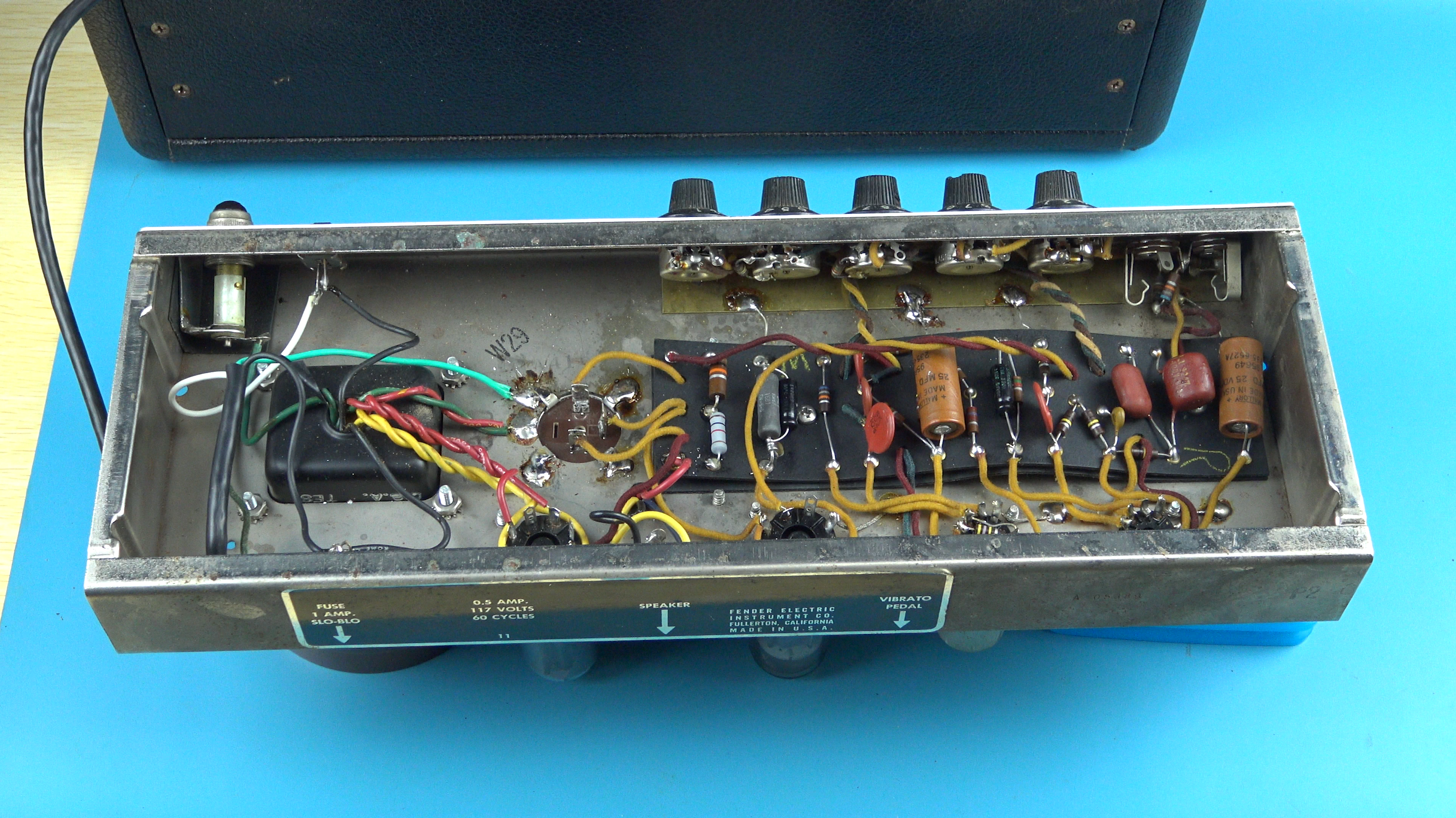
The downside of point-to-point though is that it's difficult to organize and can be limiting. To make components more uniform and decrease production time engineers came up with terminal strip construction, which is just an intermediate form of point-to-point. Instead of direct connections the components are laced through little metal terminals that come on strips or boards. Everything is then connected up with wires to where they need to go. Terminal strip construction is very solid and gives you many more options than true point-to-point.
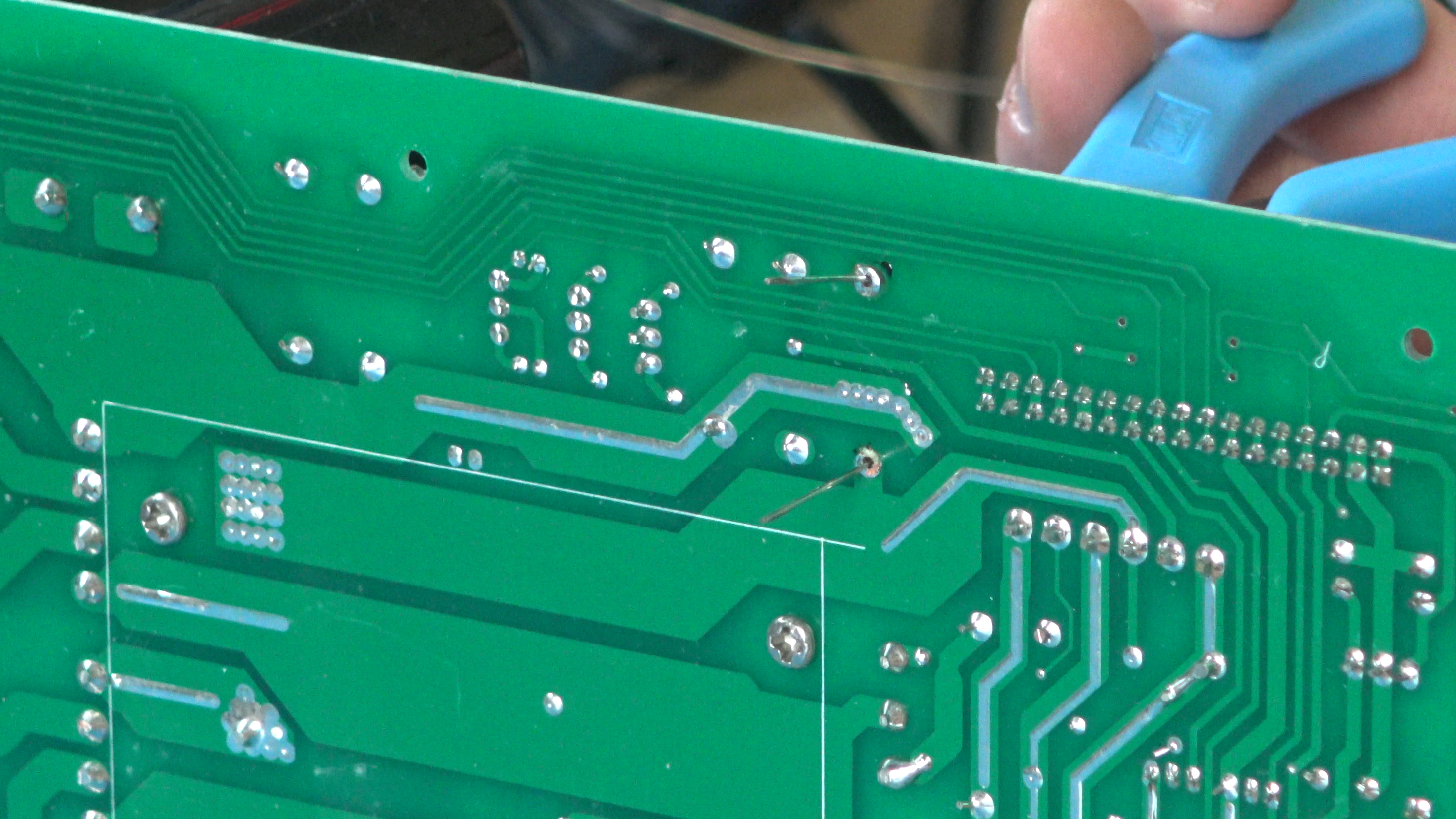
The answer to this need was the printed circuit board or PCB. PCBs allowed engineers to creatively arrange their components and link them through copper traces embedded in the board. These custom boards would be pre-drilled for the component leads and also have plated pads on the bottom to solder to. This type of construction is called plated through hole PTH or THD because the components are known as through-hole devices.
The culmination of all these electronic advancements brings us surface mount technology. SMT further improves on the space saving qualities of THD by soldering components directly to the surface of the PCB. This allows technicians to populate the top and bottom, effectively doubling the capacity of the board. Since SMD components are significantly smaller than any through-hole components, devices can be built incredibly small. The downside though is that the smaller you go though the more difficult the equipment is to service and repair.